L-R: Senior Niraj Raju (trombone), junior Andrew Simmons (tuba) and senior Julia Maas (violin) of the Montgomery County, MD Youth Orchestra - http://www.mcyo.org
Back in the 1970’s, I made a discovery that seemed unique to me. As a young teacher, musician, band, orchestra and Jazz ensemble director, it was my unexpected pleasure to discover that junior high and middle school aged students had an unbelievable capacity to learn and to excel. This discovery was recently confirmed in an article which appeared in a special edition of U.S. News and World Report, “Secrets of Your Brain,” by Nancy Shute entitled, “How to Deploy the Amazing Power of the Teen Brain.”
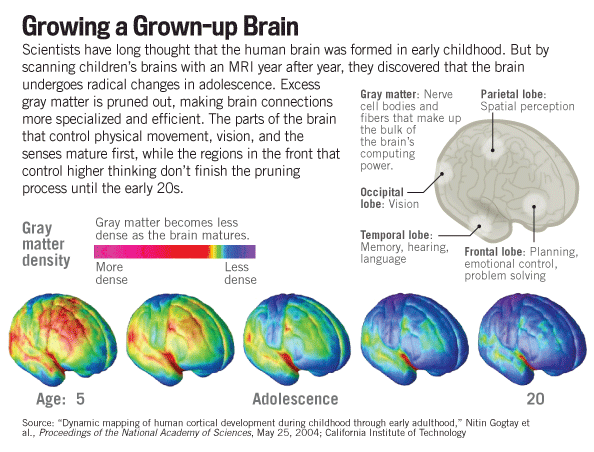
Early on in my teaching career, I discovered a mystery of life that, until Nancy’s article, seemed rather extraordinary to me, but I had no scientific evidence to back it up. Before the use of MRI’s beginning in the 1990’s, it was impossible to know what nuanced changes were occurring in the brains of teenagers, but that is not the case today. Of course, the neurologists still don’t understand all of the myriad details of change that appear to be occurring, but they can make certain not so speculative statements about these changes. According to the article, what they found astonished them. The brain’s gray matter, which forms the bulk of the structure and processing capacity, grows gradually throughout childhood, peaks around age 12, and then furiously prunes underused neurons.
Because these changes begin in the back of the brain and move forward, sensory and motor skills mature first followed by the prefrontal cortex which is responsible for judgment and impulse control. According to the scientists at the NIH, the prefrontal and cortex isn’t done until the early 20’s or later in men. The following quote from the article, however, should be the basis for all of the arts education in the United States, “Neurons, like muscles, operate on a ‘use it or lose it’ basis: a teenager who studies piano three hours a day will end up with different brain wiring than someone who spends that same time shooting hoops or playing video games. “Eureka!”
When we consider that during the teenage years, emotion and passion also heighten attention and tramp down fear, teenagehood turns out to be the perfect time to master new challenges. According to Frances Jensen, a neurologist at Children’s Hospital in Boston, “They can do things now that will set them up later in life with an enhanced skill set.” Of course, the 70’s in semi-rural America did not harbor all of the challenges that we face now for our teenagers, but challenges did exist. What I had discovered in my work was by treating the teenagers more closely as peers than subservient children, while still maintaining control, by allowing them to work with you to select and enumerate their goals, and finally by encouraging them along the way, their passions and intensity would take the music and their performances to heights that would have seemed otherwise incomprehensible.
Music arranged for teenaged performing groups was typically watered down and lacked both emotion and challenge. Because of that, it was my choice to make musical scores available to them that would have been considered too mature, too challenging and too far beyond their comprehension. The trade off, however, was that we were careful never to let them hear any of those “too hard” descriptors. The results were stupefying. The kids worked endlessly and tirelessly to make sure these musical scores were mastered. Because their parents were, in many cases, second generation immigrants, they worked to ensure that the kids had: 1.) Plenty of sleep 2.) Healthy foods 3.) No drugs or alcohol.
The U.S. News article concluded with something that was instinctive to me: “Nature had a reason to give adolescents strong bodies, impulsive natures, and curious flexible minds.” It was the stuff from which scholars, great artists and future leaders were made, and to all of my former students who have been so incredibly successful…I hope you’ve tried to give your children these same experiences!
Nick Jacobs speaks to youth on the future of healthcare
Health 2.0 Leadership (1 of 2) from Nick Jacobs, FACHE on Vimeo.